Study of the Influence of the Nature of the Solvent on the Performance of Polyethersulfone Membranes
Downloads
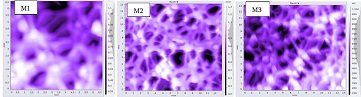
The influence of solvents dimethylformamide (DMF), dimethylacetamide (DMAc), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) on the morphology and specific productivity of membranes made on the basis of polyethersulfone (PES 5900) was studied. Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) is used as a pore-forming agent, which increases the hydrophilicity of the membrane and plays an important role in regulating various properties of the resulting polymer membrane. It is shown that membranes with different surface structure and specific productivity depending on the physicochemical nature of the selected solvents, the difference in the solubility parameters of the polymer, solvent and non-solvent. During the coagulation process, the low affinity of DMSO for PES and the high affinity for water lead to increased interaction between the solvent and non-solvent and ensure an optimal coagulation rate during the phase inversion process. Microfiltration membranes in the pore size range of 0.24-0.9 µm were obtained and tested on a laboratory setup created at the institute. In the case of using DMSO as a solvent, high-performance membranes (2184 l/m2 h) were obtained, which is 47.16% and 44.13% higher than the productivity of membranes obtained from PES/DMF/water and PES/DMAc/water systems, respectively. The process of PES dissolution was monitored using a polarization interference microscope (Biolar). The particle size, concentration and dispersion index in solutions were studied by dynamic light scattering (Zetasizer Nano Zen3690, Malvern Instruments), the structure and morphology of the membranes were studied by scanning probe (tunneling) microscopy (Certus Standard V, Nano Can Technologies).
Downloads
P. D. Amin, V. Bhanushali, S. Joshi: Role of Polyvinlyppyrrolidone in Membrane Technologies,” International Journal of ChemTech Research, vol. 11, no. 9, pp. 247–259, (2018).
Sophie Cerneauxa, Izabela Struzynska, Wojciech M. Kujawski, Michel Persina, André Larbot: Comparison of various membrane distillation methods for desalination using hydrophobic ceramic membranes, Journal of Membrane Science, 337, 55–60, (2009)
K. Elsaid, E.T.Sayed, M.A.Abdelkareem, M.S. Mahmoud, M.Ramadan: Environmental impact of emerging desalination technologies: A preliminary evaluation. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 8 (2020).
B.Keskin, T.Ormancı-Acar, T.Türken, D.Y. Imer, I. Koyuncu: Effect of wetting agent on the dye filtration performance of ultrafiltration membrane. Water Sci. Technol., (82) 577-586 (2020).
X. Wei, Z. Wang, J. Wang, and S. Wang, “A novel method of surface modification to polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane by preadsorption of citric acid or sodium bisulfite,” vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 35–49, 2012.
W. Sun, J. Liu, H. Chu, and B. Dong: Pretreatment and membrane hydrophilic modification to reduce membrane fouling, Membranes (Basel), 3, (3), 226–241, (2013).
G. BIBILEISHVILI, M. KEZHERASHVILI, N. GOGESASHVILI, L. KUPARADZE: Effect of the Temperature of the Non-Solvent on the Morphology of the Polymeric Membrane. European Journal of Scientific Research (EJSR), 161 (1), 5 (2022).
G. V. BIBILEISHVILI, M.G. KEZHERASHVILI, M.A. MAMULASHVILI: Effect of Different Solvent and Fore-Forming Agent on Morphology and Performance of Polyethersulfone Membranes. Oxidation Communications,Vol. 47, No 3, (2024).
A. K Holda, F. J. Vankelecom, Understanding and guiding the phase inversion process for synthesis of solvent resistant nano filtration membranes J. APPL. POLYM. Sci. 2015, 442,1-17
A. Abdelrasoul, H. Doan, A. Lohi, C.H. Cheng, Morphology control of polysulfone membrane sinfiltration processes: A critical review, ChemBioeng Rev., 2, 22–43, (2015)
G.BIBILEISHVILI, M.KEZHERASHVILI, N.GOGESASHVILI, L.KUPARADZE: Influence of Some Factors on Characteristics of Poly-m-phenylene-isophthalamide Membranes-Preparation and Examination of Polyamide Membranes. Oxidation Communications, 45 (2), 300 (2022).
Copyright (c) 2025 Georgian Scientists

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.


























































































































































































































